WHAT IS PNEUMONIA AND ITS TREATMENT
Pneumonia is one of the most prone to disease prevention. However, according to the World Health Organization, one child in the world dies every 20 seconds from this infection. The USA Best Doctors provide more facilities in medical field. Therefore, on the day of the fight against pneumonia, we remind you of the seriousness of this disease and offer simple steps that each of us can take to prevent the development of pneumonia in our child or ourselves.
WHAT IS PNEUMONIA
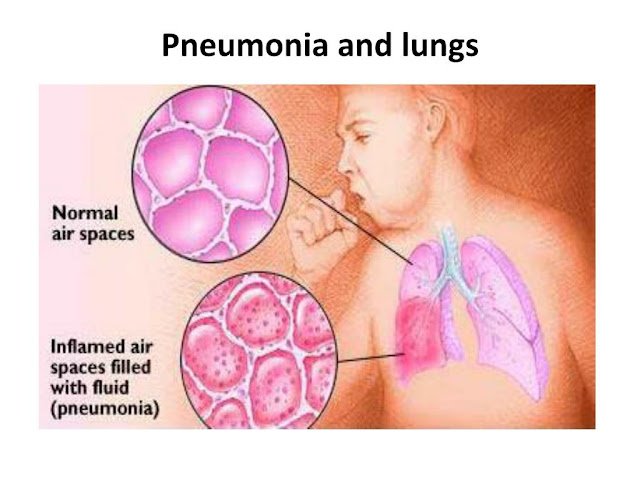
Pneumonia is an acute infectious inflammation of the lungs, localized
primarily in the air bubbles called alveoli. In a healthy person, the alveoli
are filled with air and function generally during respiration. And in patients
with pneumonia, mucus and fluid accumulate in the alveoli, which causes pain
when breathing and limits the flow of oxygen. The causative agents of pneumonia
are most often bacteria or viruses, which are usually transmitted by direct
contact with infected people.
Today, pneumonia is considered the most common and severe infectious
cause of high infant mortality worldwide. According to the WHO, pneumonia is
the cause of death in about 16% of children under five worldwide.
CAUSES OF PNEUMONIA
The most common causes of infectious pneumonia are bacteria,
viruses, fungi, and some simple microorganisms.
Thus, pneumococci (Streptococcus Pneumoniae) and Haemophilus
Influenzae type B (Hib) are the most common causes of bacterial pneumonia in
children, and the most common cause of viral pneumonia is respiratory syncytial
virus infection (acute).
Pneumonia caused by fungi such as Pneumocystis jiroveci
(pneumocystosis) is not typical, but most cases of infection are recorded in
immunocompromised patients with HIV / AIDS, especially in children. Thus, these
microorganisms cause at least a quarter of deaths from pneumonia among
HIV-infected children.
There are different ways in which pneumonia can be spread. Viruses
and bacteria, usually localized in a child's nose or throat, can enter the
lungs by inhalation. In addition, these pathogens are spread by airborne
droplets when coughing or sneezing.
Infectious pneumonia can also be contracted through the blood,
especially in infants during childbirth or immediately after birth.
SYMPTOMS OF PNEUMONIA
Most of the symptoms of viral and bacterial forms of pneumonia are
similar in general, but a patient with viral pneumonia may have a greater
variety of symptoms.
The most common symptoms of pneumonia are:
- cough,
- difficulty breathing,
- high body temperature (39
°),
- rapid breathing,
retraction of the chest, when inhaling air sinks the lower part of the
chest (in a healthy person, the chest expands when inhaled),
wheezing during breathing (more often with viral infections).
Absolutely all of these symptoms are not always present in
pneumonia.
Sometimes infants with pneumonia find it difficult to swallow or
drink, they may have a low body temperature, seizures, and sometimes children
may even faint.
PNEUMONIA IN CHILDREN:
The body's defenses often fight infection, and pneumonia does not
develop. But this applies to healthy children. But children with specific
disorders and weakened immune systems are at high risk of developing pneumonia
and its complications. This is especially true for infants who do not receive
breast milk, as the weakening of the child's immune system is often associated
with insufficient or unbalanced nutrition.
In addition, children infected with HIV or measles are at risk.
- According to the WHO, the
risk of a child developing pneumonia also increases under the influence of
the following environmental factors:
- indoor air pollution as a
result of cooking and the use of biofuels for heating;
- living in overcrowded
houses;
PREVENTION OF PNEUMONIA
Prevention of pneumonia in children is one of the main elements of the
strategy to reduce infant mortality worldwide, according to the WHO. Scheduled
vaccination is recognized as the most effective method of preventing pneumonia.
In the USA, high-quality and effective vaccines against Hib infection
(Haemophilus influenzae type B), measles (as part of the combined CPC vaccine
against measles, mumps, rubella), and pertussis are purchased at the expense of
the State budget.). Children will be vaccinated against these diseases free of
charge. There are enough vaccines in all regions of the country. Information on
vaccine residues in your area can be found here. The
Prevention of pneumonia in children and adults also involves
strengthening the immune system. First and foremost, make sure your diet is
balanced and adequate. This is especially important for newborns: breastfeeding
for the first six months of life will strengthen the baby's immunity.
Take care of cleanliness in the house, ventilate the room, quit
smoking, or do not smoke in the room and when children are around.



Comments
Post a Comment